Published by Ahmad Rizal SULTAN1, Mohd Wazir bin MUSTAFA2, Makmur SAINI3, Ahmad GAFFAR4
1,3,4 Politeknik Negeri Ujung Pandang, South Sulawesi-Indonesia
2Universiti Teknologi Malaysia, Faculty of Electrical Engineering, Johor-Malaysia
Abstract. The aim of this paper is to detect the single line to ground fault on the unit generator- transformer. A new ground fault detection scheme based on the extraction of energy and statistical parameters from wavelet transform based neural network is proposed. The faulty current signals obtained from a simulation were decomposed through wavelet analysis into various approximations and details. The simulation of the unit generator-transformer was carried out using the Sim-PowerSystem Blockset of MATLAB. The energy and statistical parameters analysis involved measured of the dispersion factors (range and standard deviation) of wavelet coefficients. Regarding the ANN performance, the errors in the SLG fault detection of ANN were under 1 %. The results indicate that the proposed algorithm was accurate enough in differentiating a single line to ground fault and un-fault for a unit generator-transformer.
Streszczenie. Przestawiono metodę detekcji nieprawidłowości w uziemieniu jednostki generator-transformator. W nowej metodzie wykorzystano transformatę falkową I sieć neuronową. Symulację przeproprowadzno wykorzystując Sim-PowerSystem Blockset of MATLAB. Uzyskano błąd pomiaru poniżej 1%. Detekcja nieprawidłowości uziemienia w jednostce generator-transformator z wykorzystaniem transformaty falkowej i sieci neuronowej
Keywords: ground-fault detection, unit generator-transformer, wavelet transform, neural network
Słowa kluczowe: nieprawidłowość uziemiania, jednostka generator-tranasformator, transformata falkowa
Introduction
Small current Ground-Fault (GF) detection has been a major concern in protective relaying for a long time. Relaying engineers and researchers often face the challenge of developing the most suitable technique that can detect faults with reasonable reliability to secure the run of a power system [1]. In general, a step up transformer at an electric power station can be categorized either as a unit generator-transformer configuration, a unit generator-transformer configuration with generator breaker, a cross-compound generator or a generator involving a unit transformer [2,3]. A GF on the transmission line or busbar can affect the system configuration of the generator.
Several methods have been reported for generator GF protection [4]. These methods have been developed based on conventional method, third harmonic method, sub-harmonic injection method and numerical protection method. Fault detection and classification algorithms based on Wavelet Transform (WT) and Artificial Neural Network (ANN) was proposed in [5, 6].
Various feature extraction methods based on WT have been used for the detection and classification of fault. Reference [6] describe fault location techniques in power system based on traveling wave using wavelet analysis and GPS timing. Fault classification algorithm based on energy and wavelet entropy in transmission have been proposed in [7, 8]. Reference [9-11] describe the feature extraction method based on fast WT, a fault index and wavelet power for use to detect the stator faults in the synchronous generator. Extraction of a statistical parameter as fault detection has been used for fault detection in previous studies, but only used standard deviation, kurtosis and skewness [12]. Meanwhile, the statistical feature parameters include kurtosis, skewness, crest factor, clearance factor, shape factor, impulse factor, variance, square root amplitude value and absolute mean amplitude value to fault diagnosis in rotating machine as described in reference [13]. The new approach as proposed in this paper includes energy and dispersion factor of statistical parameters on single-line to ground (SLG) fault detection.
The novel method for GF detection uses energy and dispersion factor of statistical parameters, which involve calculating the Energy, Range (R) and Standard Deviation (STD) values of wavelet coefficients, which are included the analysis in this paper. In the analysis, the GF signals were computed by using Discrete Wavelet Transform (DWT). The GF detection was carried out through the analysis of value of energy, R and STD of the current wavelet coefficients, including the detail and approximate of wavelet coefficients to distinguish SLG-fault.
Energy and Statistical Parameters Extraction Method
A WT is a powerful tool for feature extraction of the transient signals. WT has been applied in many literatures for feature extraction of transient fault signals. The differences among modifications of this method are: different types of mother wavelet, various numbers of decomposition level, and state of calculating the energy or entropy features. There are many types of mother wavelets such as Haar, Daubechies, Symlets, Meyer, Dmeyer, Morlet. The optimal choice of the mother wavelet plays a significant role for detection various types of transient signals. The optimum wavelet for extracting signal information is that can generate as many coefficient as possible to represent the characteristic of signals. In this paper, DWT was used for feature extraction, which provided high time and low frequency resolution for high frequency and high-frequency resolution and with low time resolution for low frequencies. The DWT was calculated by using the following equation [14]:

where “g(k)” is the mother wavelet, “x(k)” is the signal input and a,b are the scaling and translation parameters.
DWT was implemented by using high-pass filter and lowpass filter respectively [15], defined as:

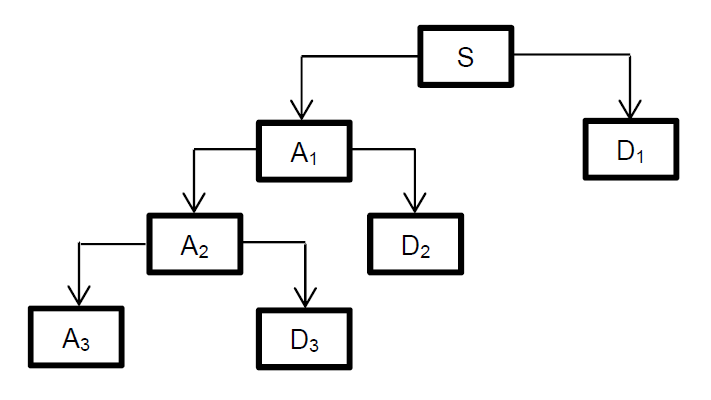
where “yhigh(k)” is the output from the high-pass filter called Detail (D) and “ylow(n)” is the output from the low-pass filter called Approximation (A). For the 3-level decomposition, the original signal is split as shown in Figure 1. The original signal S is represented as A1 + D1, A2 + D2 + D1, A3 + D3 + D2 + D1.
The mean idea of making a feature extraction is to reduce the amount of information, either from the original waveform or from its transformation format. In this study, for feature extraction process, the coefficient features of wavelet such as wavelet energy, R and STD value of wavelet coefficient had to be calculated.
a. Wavelet Energy
The wavelet energy is the sum of square of detailed wavelet transform coefficient [16]. The energy of a wavelet coefficients is varying over different scales depending on the input signals. The wavelet energy of coefficient c(t) can be defined as follows:
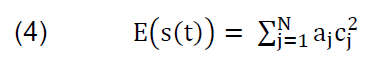
with appropriate scaling coefficients aj for the coefficient cj obtained from the corresponding signal “s(t)”. The energy of signals is contained mostly in the approximation part and a little in the detail part [17]. For example, the approximation coefficient at the first-level contains more energy than the other coefficients at the same level of the decompositions tree. Because the faulty signals have high-frequency components, it is more distinctive to use energy of detail coefficients [18].
b. Dispersion Factor of Statistical Parameters
In descriptive statistics, the concept of range has a more complex meaning. The range is the size of the smallest interval which contains all the data and provides an indication of statistical dispersion. It is measured in the same units as the data. Since it only depends on two of the observations, it is most useful in representing the dispersion of small data sets [19].
STD is a number used to tell how measurements for a group are spread out from the average, or expected value. The STD of statistical parameters in wavelet detail coefficients are estimated from the equations:
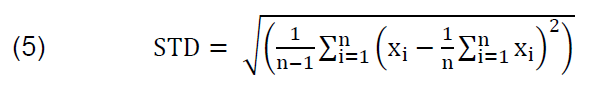
where “x” is the data vector and the “n” the number of elements in that data vector. The STD of the output signals is the square root of the data vector variance. This feature provides information about the level of variation of the signal frequency distribution [20].
Artificial Neural Network Pattern Recognition
ANN is very good at pattern recognition problems. An ANN with enough elements can classify any data with arbitrary accuracy. They are particularly well suited for complex decision boundary problems over many variables [21]. The use of pattern recognition for power system security analysis was first investigated in 1968. Since ANN can fully be applied for pattern recognition, they have been widely investigated for transient classification [22]. The ANN can be used to solve power system protection problems, particularly those where traditional approaches have difficulty achieving the desired speed, accuracy, and selectivity [23-25]. Pattern recognition for partial discharge in GIS based on pulse coupled neural networks and wavelet packet decomposition have been proposed in [26].
In pattern recognition problem, a neural network can be used to classify input into a set of target categories. In this paper, a set input of energy wavelet coefficient and dispersion factor in statistical parameters of wavelet coefficients are used for input against set ground-fault or un-fault target categories.
Proposed Method
The block diagram of proposed SLG-fault detection algorithms is shown in Figure 2. The first step of the detection module was to get the current samples from Sim-PowerSystem Blockset of MATLAB simulation. The fault current signals were then computed by DWT. The fault detection was carried out through the analysis feature extraction of dispersion factor or the current energy of wavelet coefficients. Feature extraction of dispersion factor and the energy of the wavelet coefficients are analysed for comparison. The block diagram is explained in steps:
– Step 1: The fault current signals are obtained from a simplified power system model (Figure 3) for GF simulation using Matlab-Simulink.
– Step 2: DWT of the fault signals are obtained and analysis using MATLAB software.
– Step 3: The wavelet coefficients of the fault signals are obtained using signal decomposition.
– Step 4: The extraction of energy and dispersion factor of statistical parameters (R and STD value) of wavelet coefficients from WT in various fault simulations are fed to ANN and trained.
– Step 5: Energy and statistical parameters of WT based ANN distinguishes GF from normal condition.

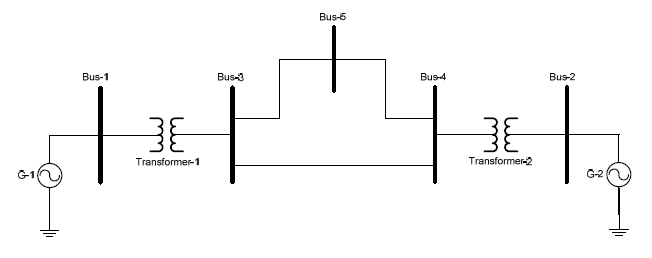
A suitable unit generator-transformer model is required to characterize the different condition during SLG-fault. GF simulations were established using Sim-PowerSystem Blockset of MATLAB, where M-file MATLAB was used for GF detection. The simulated power system models for GF simulation are shown in Figure 3. The data of a generator (G1=G2) 25 kV with various generator grounding method, the transformer (transformer- 1=transformer-2) 25/150 kV with Yn-Yn transformer connections. Simulation was carried out at various fault locations includes primary and secondary side of a transformer-1, and at generator bus. Fault current was taken from the generator bus (Bus-1).
Analysis of Simulation Results
Designing SLG-fault detection on unit generator-transformer models follows a number of systemic procedures. In this paper, there are three basics steps:
(1) signals decomposition, (2) feature extraction and (3) ANN trained and verified.
(1). Signals Decomposition
In this paper, the energy and dispersion factor of statistical parameters features obtained by WT for faulty signals have been used as input for the ANN. If the wavelet coefficients are used as input to the ANN, it will result in rather large number of inputs posing difficulty for training and testing of ANN in connection with accuracy and speed. Therefore, the energy and dispersion factor of wavelet coefficients have been used as inputs to the ANN instead, in order to overcome this problem but retaining important feature of wavelet signals.
In some studies, Daubechies mother wavelet has good ability to capture the transient events and frequency feature extraction during fault in the power system. In this paper, the mother wavelet db3 with resolution level 3 used to obtain the coefficient of DWT for SLG-fault detection in unit generator-transformer. Some model for the original signal and parts of the coefficient with resolution level 3 of DWT db3 as illustrate in Figure 4 and Figure 5 respectively.
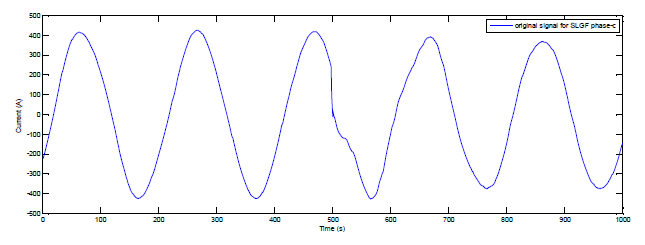

(2). Features Extraction
The main idea of making a feature extraction is to reduce the amount of information, either from the original signals of from its transformation format. To reduce the number of ANN processing element, in this paper used a new approach of an energy and dispersion factor (R and STD value) of statistical parameters of wavelet coefficient for ANN input.
After getting the wavelet coefficient of the fault signals was obtained using signal decomposition, the next step in the extraction of the energy and dispersion factor of statistical parameters of the wavelet coefficients from WT in various fault simulations. Applying the energy and dispersion factor of each decomposition level, the numerical value of patterns can be obtained from analysed signal, as it is shown in Table 1 and Table 2 respectively.
Table 1. Energy feature vector of SLG-fault
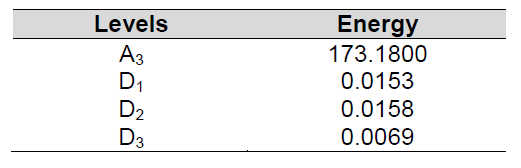
Table 2. Dispersion factor feature vector of SLG-fault

The feature vector characteristics of each factor are then used as inputs for the ANN. In this case, 3000 signals were used for energy feature and 12000 signals were used for dispersion factor feature.
(3). ANN Trained and Verified
ANN has proven to very efficient in the field of classification. In this paper, the pattern recognition algorithms are used for classifying SLG-fault current and normal current condition in the unit generator-transformer. Pattern recognition is the process of training a neural network to assign the correct target classes to a set of input patterns. Once trained the network can be used to classify patterns it has not seen before.
MATLAB program has been developed for training process. The kinds of sample are divided into three namely training sample, validation sample, and testing sample. Training samples are presented to the network during training, and the network is adjusted according to its error. Validation samples are used to measure network generalization, and to halt training when generalization stops improving. Testing samples have no effect on training and so provide an independent measure of network performance during and after training.
The network has to detection of GF-fault at the various conditions of a unit generator-transformer. The inputs for network are extracting from dispersion factor of statistical parameters and energy of current details of wavelet coefficients. The WT is done to reduce the number of ANN processing element, and accordingly, it will reduce the time consumed for training and testing of the ANN. Moreover, it also helps to achieve high-performance detection.
The behaviour of the selected ANN depends on numerous parameters, such as the number of hidden layers, the number of hidden neurons, transfer function, initial weights and biases, training rule and training parameters. Table 3 shows the features of the constructed network. Two types of network were used for analysis with a number of different inputs. Model based on various input parameters as described in Table 4. 3000 sets of sample (70 % sets for training, 15% sets for validation and 15% set for testing) are used for energy wavelet coefficient network and 12000 sets of sample (70 % sets for training, 15% sets for validation and 15% set for testing) were used for R wavelet coefficient, STD wavelet coefficient or combined R and STD for ANN network.
Table 3. Features of the constructed network
Table 4. Models based on different input parameters

While training the network, energy and dispersion factor of wavelet coefficients pattern corresponding to varied conditions such as fault resistance, fault initiation time, and various generator grounding method are used. The targets for normal currents condition are trained to be ‘0‘, and the target for SLG-fault currents are trained to be ‘1’. Target vector is assigned value ‘1’ or ‘0’ according to the network condition. Threshold is set at 0.5. I.e values above 0.5 are treated as ‘1’ and values below 0.5 are treated as ‘0’. Once performance goals are met, an unknown pattern is applied to verify whether the network is trained properly or not.
The designed ANN is trained for various training patterns of normal and SLG-fault conditions. Various architectures were attempted to arrive at the final architecture with a goal maximum accuracy. After much experimentation, for ground fault detection six different architectures were developed and used for training. After enough experimentation, it was inferred that the architecture with one hidden layer of 20 neurons and one output was giving the optimum results. The goal of 0.0712 error is a achieved in 184 iterations during 27 seconds. Figure 6 Shows the graph between training performance and number of iterations to train the designed 4-20-1 of ANN structure.
Fig.6. Best validation performance energy as input for 4-20-1 of ANN structure
The performance of trained network for various architecture can be measured, to some extent, by the errors on the training, validation, and test sets. Comparison of mean squared error (mse) parameters of a pattern recognition model in various ANN structures as illustrate in Table 5.
Table 5. Mean squared error parameters of pattern recognition models for various network structures
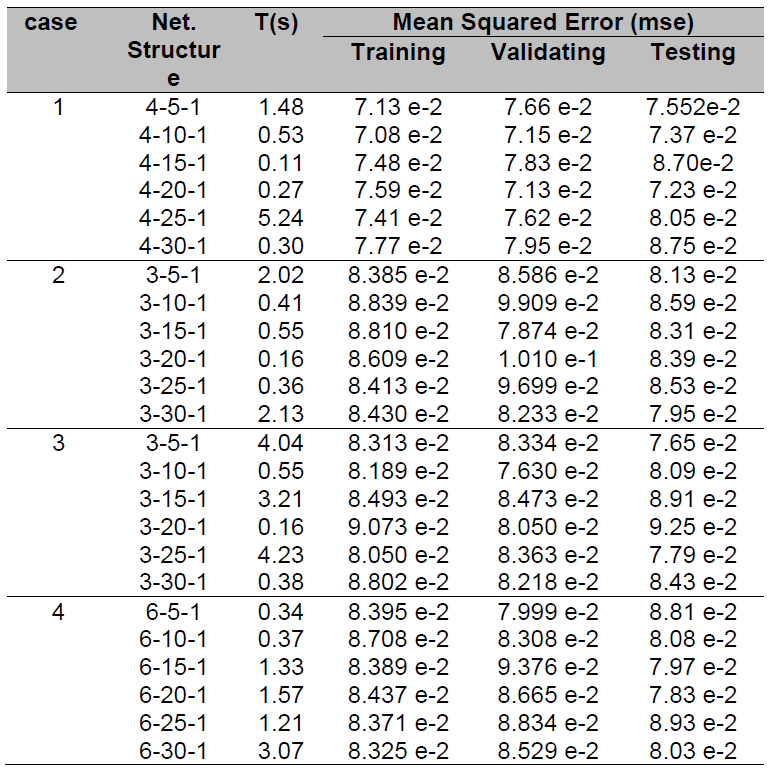
From the Table 5, it appears that the case-1 result valid performance for testing SLG-fault signals than the case-2, case-3 and case-4. By using energy as ANN input, detection of the SLG-faults on the generator unit transformers was accurate enough in differentiating the SLG-fault and un-fault for a unit generator-transformer compared to R and STD value as input ANN.
Conclusion
This paper has presented a novel approach for SLG-fault detection at the unit generator-transformer. Regarding the ANN performance, the errors in the SLG-fault detection of ANN were under 1 %. In this paper, analysis of energy wavelet coefficients successfully applied to distinguish SLG-fault at the unit generator-transformer. The statistical parameters involved calculating the dispersion factors (R and STD value) of DWT were available to detect the GF.
REFERENCES
[1] Omar A.S, Youssef. Online Application of Wavelet Transforms to Power System Relaying. IEEE Transactions on Power Delivery 2003; 18: 1158-1165.
[2] IEEE Std C37.102™-2006, IEEE Guide for AC Generator Protection.
[3] J.C.Das. Power System Relaying. Wiley Encyclopedia of Electrical and Electronic Engineering, 1999.
[4] A.R.Sultan & M.W.Mustafa. Ground Fault Protection Methods of a Generator Stator. Przeglad Elektrotechniczny 2013; 10: 225-229.
[5] Silva.K.M, Souza.B.A, Brito.N.S.D. Fault Detection and Classification in Transmission Lines Based on Wavelet Transform and ANN. IEEE Transactions on Power Delivery 2006; 21 : 2058-2063.
[6] Amir T, Mohammad-Reza M., & Abdolreza R. Fault Location Techniques in Power System based on Traveling Wave using Wavelet Analysis and GPS Timing. Przeglad Elektrotechniczny 2012; 6 : pp.347-350
[7] H.Zhengyou, G.Shibin, C.Xiaoqin, Z.Jun, B.Zhiqian & Q.Qingquan. Study of a new method for power system transients classification based on wavelet entropy an neural network. Electrical Power and Energy Systems 2011; 33: 402-410.
[8] Safty S.E, El-Zonkoly A. Applying wavelet entropy principle in fault classification. Electrical Power and Energy System 2009; 31: 604-607.
[9] Pittner.S, Kamarthi.S.V. Feature Extraction From Wavelet Coefficients for Pattern Recognition Tasks. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence 1999; 21: 83-88.
[10] Rao.P.V.R, Gafoor SA. Wavelet ANN based stator ground fault protection scheme for turbo generators. Electric Power Components and Systems 2007; 35: 575-59.
[11]Rahman, M.A, Ozgonenel O & Khan M.A. Wavelet transform based protection of stator faults in synchronous generators. Electric Power Components and Systems 2007; 36: 625-637.
[12]Baqui I, Zamora I, mazon J & Buigues G. High impedance fault detection methodology using wavelet transform and neural network. Electrical Power System Research 2011; 81: 1325-1333.
[13]S.Changqin, Wang.D, Kong.F & Tse.P.W. Fault diagnosis of rotating machine based on statistical parameters of wavelet packet paving and a generic support vector regressive classifier. Measurement 2013; 46: 1551-1564.
[14]Chul-Hwan Kim, Hyun Kim, Young-Hun Ko, Sung-Hyun Byun, Raj K. Aggarwal and Allan T. Johns. A Novel Fault-Detection Technique of High-Impedance Arcing Faults in Transmission Lines Using the Wavelet Transform. IEEE transactions on power delivery 2002; 17.
[15] Robi Polikar. The Story if Wavelets. Iowa State University
[16]Morchen, F. Time series feature extraction for data mining using DWT and DFT, Technical Report, No.33, Department of Mathematics and Computer Science, University of Marburg, Germany, 2003
[17]Pham,T.V & Kubin,G. DWT-based classification of acousticphonetics classes and phonetic units. In proceeding of ICSLP’04 South Korea, 2004: 985-988.
[18]Ekici, S., Yildirim S., Poyraz M. Energy and entropy-based feature extraction for locating fault on transmission lines by using neural network and wavelet packet decomposition. Expert Systems with Applications 2008; 34: 2973-2944.
[19] Viljoen C. Elementary Statistic Vol. 2 Pearson South Africa, 2000
[20]Baqui I, Zamora I., Mazon J., & Buigues G. High impedance fault detection methodology using wavelet transform and artificial neural network. Electric Power System Research 2011; 81: 1325-1333.
[21] MATLAB reference manual. The Mathworks Inc, 2012
[22]Othman,M., Mahfout,M., & Linkens,D. Transmission line fault detection, classification, and location using an intelligent power system stabiliser. IEEE Int. Conf. Elect. Utility Deregulat 2004; 1: 360-365.
[23]Coury,D.V., Oleskovicz,M., & Aggarwal,R. K. An ANN routine for fault detection, classification, and locating in transmission lines. Electric Power Component System 2002; 30: 1137-1149.
[24]Reaz, M., Choong, F., Sulaiman, M., Mohd-Yasin, F., & Kamada, M. Expert system for power quality disturbance classifier. IEEE Trans. Power Delivery 2007; 22: 1979-1988.
[25]Al-Shaher., M. Saleh, A.S & Sabry, M.M. Estimation of fault locating and fault resistance for single line-to-ground faults in multi ring distribution network using artificial neural network. Electric Power Component System 2009; 37: 697-713.
[26] Jiabin Z., Ju T., Xiaoxing Z., & Jiagui T., Pattern recognition for partial discharge in GIS based on pulse coupled neural networks and wavelet packet decomposition, Przeglad Elektrotechniczny 2012; 5b : pp.44-47
Authors: Ahmad Rizal Sultan, Politeknik Negeri Ujung Pandang, South Sulawesi, Indonesia 90245, E-mail: rizal.sultan@poliupg.ac.id Mohd Wazir Mustafa, Faculty of Electrical Engineering, Universiti Teknologi Malaysia(UTM), Skudai, Malaysia 81300. Makmur Saini, Politeknik Negeri Ujung Pandang, South Sulawesi, Indonesia. Ahmad Gaffar, Politeknik Negeri Ujung Pandang, South Sulawesi, Indonesia.
Source & Publisher Item Identifier: PRZEGLĄD ELEKTROTECHNICZNY, ISSN 0033-2097, R. 94 NR 12/2018. doi:10.15199/48.2018.12.07